A deck of cards has 13 face values: Ace, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, Jack, Queen, and King. These face values are present for four different suits (Clubs, Diamonds, Hearts, and Spades) for a total of 52 cards.
An event's probability in an experiment with equally likely outcomes is defined by the following formula, where P (event) means the probability of the event occurring and is founding by dividing the number of outcomes in the event by the number of outcomes in the sample space:
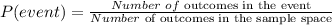
The probability of not getting the event is given to be:
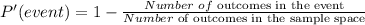
Since there are 4 cards with a face value of 9, the probability of getting a 9 is:
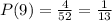
Therefore, the probability of not getting a 9 is given to be:
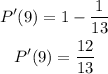
In two decimal places, the probability that the card picked does not have a face value of 9 is 0.92.