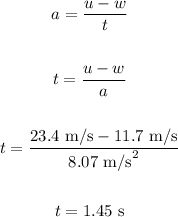Given:
The initial velocity of the car is: u = 0 m/s
The final velocity of the car is: v = 23.4 m/s
The velocity of the car changes over the time t = 2.90 s
To find:
a) The magnitude of the car's acceleration
b) The time taken by a car to change its speed from 11.7 m/s to 23.4 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The acceleration of the object is defined as the rate of change of its velocity.
a)
Mathematically the acceleration of the car is given as:
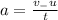
Here, a is the acceleration of the car.
Substituting the values in the above equation, we get:
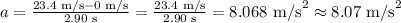
b)
The car accelerates uniformly, thus, the acceleration of the car when its velocity changes from zero to 23.4 m/s will remain the same.
Let w be the initial velocity. Thus,
w = 11.7 m/s
The time taken by the car to change its speed from 11.7 m/s to 23.4 m/s can be determined as: