Answer:
To determine the number of solutions, we have to solve each equation for x.
1.- To solve the equation for x, first, we apply the distribute property on both sides of the equation:
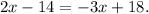
Adding, 3x to both sides of the equation, we get:
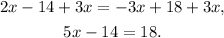
Adding 14 we get:
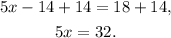
Dividing by 5, we get:
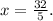
Therefore, the equation has one solution.
2.- Applying the distributive property on the right side of the equation, we get:
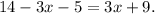
Adding like terms, we get:
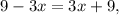
therefore, by properties of real numbers,
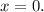
The equation has 1 solution.
3.- Applying the distributive property on the right side of the equation, we get:
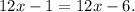
Subtracting 12x from both sides of the equation, we get:
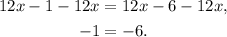
The above equality is a contradiction, therefore the equation has no solutions.
4.- Applying the distributive property on the left side of the equation, we get:
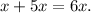
Simplifying the above equation, we get:

Since the above equality is always true for any value of x, then the equation has infinitely many solutions.
5.- Applying the distributive property on the left side of the equation, we get:
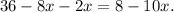
Adding like terms, we get:
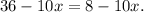
Adding 10x to both sides of the equation, we get:
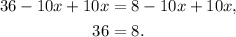
The above equality is a contradiction, therefore the equation has no solutions.