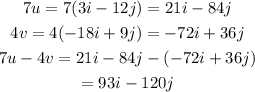PART A:
The linear form of a vector is given by:
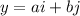
Where i indicates the horizontal direction and j indicated the vertical direction.
To find the values of a and b, let's find the horizontal and vertical distances between the points.
For vector u, we have:
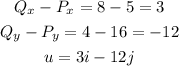
For vector v, we have:
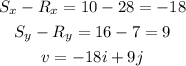
PART B:
To find the trigonometric form, we need the magnitude and angle of each vector:
![\begin{gathered} \text{ vector u:} \\ |u|=\sqrt[]{3^2+(-12)^2}=\sqrt[]{9+144}=\sqrt[]{153} \\ \theta=\tan ^(-1)((-12)/(3))=-75.96\degree \\ u=\sqrt[]{153}(\cos (-75.96\degree)i+\sin (-75.96\degree)j) \\ \text{vector v:} \\ |v|=\sqrt[]{(-18)^2+9^2_{}}=\sqrt[]{324+81}=\sqrt[]{405} \\ \theta=\tan ^(-1)((9)/(-18))=-26.57\degree \\ v=\sqrt[]{405}(\cos (-26.57\degree)i+\sin (-26.57\degree)j) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/uru2iwwqy33zqzq6rgtx4t129tmuumxkhv.png)
PART C:
Calculating the given operation, we have: