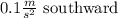First, find the net force acting on the object by adding the individual forces exerted on it (as vectors):
Take the vectors pointing to the south as negative and those pointing to the north as positive. Then, the magnitude of the net force acting on the object, is:
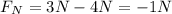
Use the magnitude of the net force to find the magnitude of the acceleration using the Newton's Second Law of Motion:
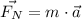
Isolate the acceleration from the equation and substitute F_N=-1N and m=10kg:
![\begin{gathered} \Rightarrow\vec{a}=\frac{\vec{F_N}}{m} \\ =\frac{-1N}{10\operatorname{kg}} \\ =-0.1(m)/(s^2) \end{gathered}]()
The direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force.
Therefore, the acceleration of the object is: