Answer:
![97.67\operatorname{cm}^3]()
Explanations:
According to Charle's law, the volume of the given mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature provided that the pressure is constant. Mathemically;
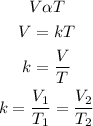
where;
V1 and V2 are the initial and final volume of the gas
T1 and T2 are the initial and final temperatures of the gas (in Kelvin)
Given the following parameters:
![\begin{gathered} V_1=100\operatorname{cm}^3 \\ T_1=27^0C=27+273=300K \\ T_2=20^0C=20+273=293K \\ V_2=\text{?} \end{gathered}]()
Substitute the given parameters into the formula;
![\begin{gathered} V_2=(V_1T_2)/(T_1)^{} \\ V_2=(100*293)/(300) \\ V_2=(29300)/(300) \\ V_2=(293)/(3) \\ V_2=97.67\operatorname{cm}^3 \end{gathered}]()
Therefore the volume of the gas at 20°C is approximately 97.67cm³