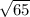
Step-by-step explanation
Step 1
Free body diagram
so, we have a rigth triangle, we can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotensue.
the theorem that the sum of the squares on the legs of a right triangle is equal to the square on the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle),so
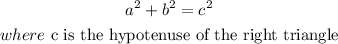
so
Let
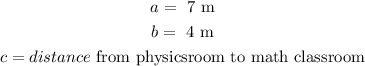
now, replace and solve for c
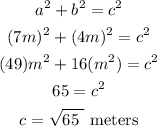
therefore, the answer is
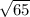
I hope this helps you