ANSWER and EXPLANATION
We want to prove that:
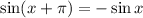
Let us start with the left-hand side of the equation.
Using trigonometric identities for sine, we have that:
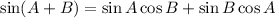
Applying this identity to the left-hand side of the equation:
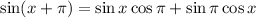
We know that:
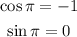
Substituting those values into the above expression:
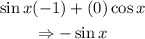
Since the left-hand side of the equation is equal to the right-hand side, we have that it has been proven.