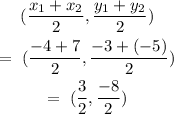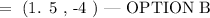SOLUTION:
Step 1:
In this question, we are given the following:
What is the midpoint of a line segment with the endpoints (-4,-3) and (7,-5)?
A. (-3.5, 1)
B. (1.5,-4)
C. (-4,1.5)
D. (1.-3.5)
Step 2:
The midpoint of a line segment with the endpoints (-4,-3) and (7,-5) is: