Let's begin by listing out the information given to us:
The figure before us is triangle. It is worth noting that the sum of angles in a triangle is 180 degrees
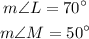
To find the angle at K (m∠LKM), we will subtract the sum of angles L & M from 180 degrees (the sum of angles in a triangle). We have:
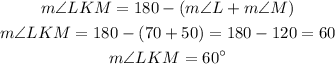
To find the angle at LKN (m∠LKN), we will subtract angle LKM from 180 degrees (the sum of angles on a straight line). We have:
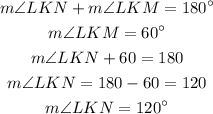
Therefore, m∠LKN is equal to 120 degrees