The test you are running is:
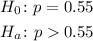
Then, you have a right-tailed p-value, then:
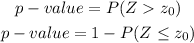
By replacing p-value =0.55:
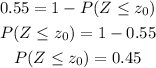
Then, in a standard normal table look for the corresponding z:
As you can see, z=-0.12 has a p-value=0.4522 and z=-0.13 has a p-value=0.4483.
Then, the average will be:
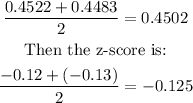
Answer: the test statistic z=-0.125