Answer
About a 8.91% decrease
Procedure
The initial temperature is 15 °C, raising the temperature by 5 °C results in 20 °C.
Therefore we read 2 values on the table the dissolved oxygen at 15 °C and the dissolved oxygen at 20 °C.
From the table, we see that at 15 °C we have about 10.1 mg/L of dissolved oxygen.
From the table, we see that at 20 °C we have about 9.2 mg/L of dissolved oxygen.
The percent decrease is calculated as follows
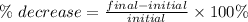
Substituting the values we have that
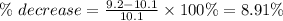
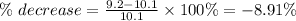
The result can be negative or preceded by the word a decrease of.