Given data
*The given mass of the hockey puck is m = 250 g
*The puck moves at a speed is v_1 = 75 m/s
*The other given mass of the second puck is M = 500 g
*The second puck is moving at a speed in the -y-direction is v_2 = 25 m/s
Objects stick together after perfectly inelastic collision.
The x-component of the final velocity of the first puck is calculated as
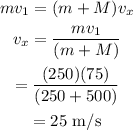
Similarly, the 'y-component' of the final velocity of the second puck is calculated as
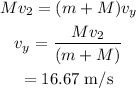
The formula for the magnitude of the velocity of both the pucks is calculated as
![\begin{gathered} v=\sqrt[]{v^2_x+v^2_y} \\ =\sqrt[]{(25)^2+(16.67)^2} \\ =30.04\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/high-school/xt0ul3bgofnusmzsb01ckuuencfia09m1p.png)
The kinetic energy lost in the collision is calculated as
![undefined]()