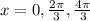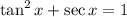
Given the next trigonometric identity:
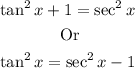
Substituting this identity into the equation:
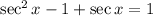
Subtracting 1 at both sides of the equation:
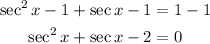
Replacing with:
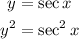
we get:
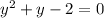
Applying the quadratic formula with a = 1, b = 1 and c = -2:
![\begin{gathered} y_(1,2)=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a} \\ y_(1,2)=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt[]{1^2-4\cdot1\cdot(-2)}}{2\cdot1} \\ y_(1,2)=\frac{-1\pm\sqrt[]{9}}{2} \\ y_1=(-1+3)/(2)=1 \\ y_2=(-1-3)/(2)=-2 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/jojqoweb1vep7fjn1qkerh1sj4nfiz9e11.png)
Recalling that y = sec(x), then we have two options:
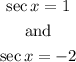
By definition:
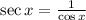
Therefore, the first option is:
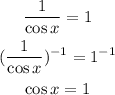
In the interval of x [0,2π), the solution to this equation is 0.
Now, considering the second option:
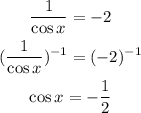
In the interval of x [0,2π), the solutions to this equation are 2π/3 and 4π/3.
In summary, the solutions to tan^2(x) + sec(x) = 1 are: