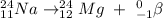Chemistry -> Nuclearchemistry -> Radioactivity
Beta decay is a type of radioactive decay that consists of the emission of a beta particle from the nucleus of an atom.
A beta particle consists basically of an electron, so it can be stated as the following:
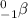
Having this concept in mind, we can write the nuclear equation focusing on keeping the equation balanced in terms of atomic number and atomic mass.
For that, we have to sum the atomic masses from both particles on each side and do the same with the atomic numbers.
Sodium-24 is an isotope of Na-23, and it has an atomic number of 11, and an atomic mass of 24.
By summing the atomic numbers, we discover that the element that will be on the red spot drawn above will have an atomic number of 12.
The element with an atomic number of 12 is Magnesium (Mg).
As for its atomic mass, it has to be 24 so it is balanced. The final equation is then the following:
Final answer: