In the given Isosceles triangle,
AB = BC
Since, from the property of issoceles triangle
Angle opposite to equal sides of a triangle are always equal,
So, in the given figure
Angle Opposite to side AB is angle C
Angle Opposite to side BC is angle A
so, Angle A = Angle C
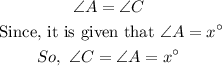
The sum of all angles in a triangle is equal to 180 degrees
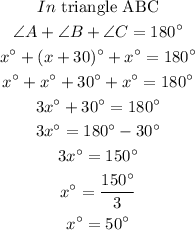
Answer : b) x = 50