Given data
*The given time interval is t = 2.62 s
*The given angular velocity is
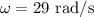
*The given number of revolutions is 9 revolutions.
The formula for the constant angular acceleration is calculated by the rotational equation of motion as
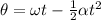
Substitute the known values in the above expression as
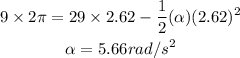
Hence, the constant angular acceleration is 5.66 rad/s^2