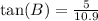Notice that the triangle △ABC is a right triangle. The side AB is the hypotenuse of the triangle, since it is opposed to the right angle C.
The tangent of the angle B is given by the ratio of the lengths of the side opposite to it and the side adjacent to it. Then:
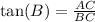
From the Pythagorean Theorem, we know that:
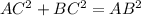
Substitute the values AC=5 and AB=12 and solve for BC:
![\begin{gathered} 5^2+BC^2=12^2 \\ \Rightarrow BC^2=12^2-5^2 \\ \Rightarrow BC^2=144-25 \\ \Rightarrow BC^2=119 \\ \Rightarrow BC=\sqrt[]{119} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/tgmt6i5bargl9wyk8hs091y9d5miw3taw4.png)
Once we know the value of BC, substitute the lengths of AC and BC to find the tangent of B:
![\tan (B)=\frac{5}{\sqrt[]{119}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/d6pua5gcebootya5eh1fgorocxeidg66rr.png)
Since the square root of 119 is approximately 10.9, then: