Given:
The value of each of the parallel resistances is,
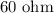
The resistance in series with it is,
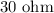
The potential difference across the combination is,
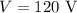
To find:
The potential drop across the parallel portion
Step-by-step explanation:
The circuit diagram looks like:
The equivalent resistance of the circuit is,

The current through the circuit is,
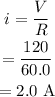
The potential drop across 30.0 ohm is,
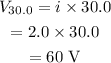
The potential drop across the rest parallel portion is,
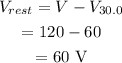
Hence, the voltage drop across the entire parallel portion is 60 V.