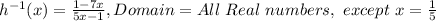Answer:
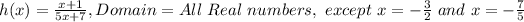
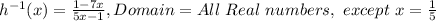
Step-by-step explanation:
The notation for composition of functions is:
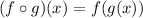
In this case:
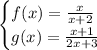
To do the composition, we replace the x in the f(x) with the function g(x):
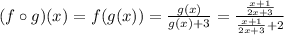
And solve:
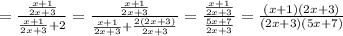
Here, we can calcualte the domain. The function is not defined when teh denominator is 0, thus:
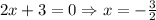
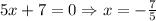
Since the function can't be evaluated when x = -3/2, we can cancel the terms (2x+3) in the numerator and denominator:
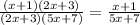
Thus:
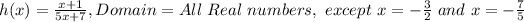
Now, to find the inverse of the function, we first switch the variables:
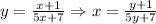
And solve for y:
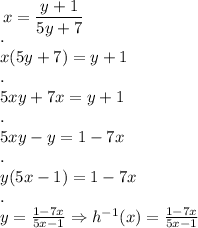
And since the denominator can't be 0:
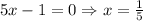
Thus: