Answer:
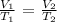
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to select the option that represent the mathematical equation of the Charles' law
According to the law, the volume of a given mass of gas at a constant temperature is directly proportional to the absolute temperature (temperature in Kelvin) of the given mass of gas
Mathematically:
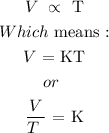
Writing the above in terms of the final and initial state, we have it that:
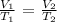
Where:
V1 is initial volume
T1 is the initial temperature
V2 is the final volume
T2 is the final temperature