You can identify that the triangle shown in the picture is a Right triangle.
You can use the following Trigonometric Identity:
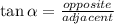
In this case:
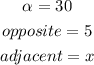
See the picture below:
Substitute values into
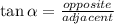
And solve for "x":
![\begin{gathered} \tan (30\degree)=(5)/(x) \\ \\ x\tan (30\degree)=5 \\ \\ x=(5)/(\tan(30\degree)) \\ \\ x=5\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/9polzqepozga5bg0h01ub03znfmqhazh7y.png)
To find the length of the hypotenuse, you can use the Pythagorean theorem:
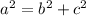
Where "a" is the hypotenuse and "b" and "c" are the legs of the Right triangle.
In this case:
![\begin{gathered} a=y \\ b=5 \\ c=5\sqrt[]{3} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/708ume8gew7f4k5a76whcib9t2p7gxofsp.png)
Substituting values into the equation and solving for the hypotenuse, you get that this is:
![\begin{gathered} y^2=(5)^2+(5\sqrt[]{3})^2 \\ y=25+25(3) \\ y=\sqrt[]{100} \\ y=10 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/43cqkdm7hobr70kgcolqdsjy752fw13ytf.png)
The perimeter of a triangle can be found by adding the lengths of its sides. Then, the perimeter of this triangle rounded to the nearest tenth, is:
![\begin{gathered} P=5m+5\sqrt[]{3}m+10m \\ P=23.66m \\ P\approx23.7m \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/tgdz9ub1awu3sapyorp09tqa2bd73vsbd3.png)
The answer is: Option C.