Answer
714.34 grams
Step-by-step explanation
Given:
Volume of the solution, V = 4.00 L
Molarity of the solution =0.55 M
What to find:
The mass of the solute required to make the solution.
Step-by-step solution:
Step 1: Calculate the mole of the solute.
The moles of the solute can be determined using the molarity formula:
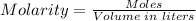
Plugging the values of the parameters into the formula:
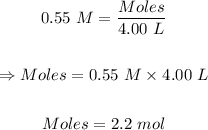
Step 2: Convert the moles of solute to the mass of solute:
Using the mole formula, the mass of the solute can be calculated as follows:
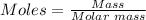
Using the atomic mass of each element in the periodic table, the molar mass of Hg(NO3)2 = 324.7 g/mol.
Putting mole = 2.2 mol and molar mass = 324.7 g/mol, the mass of the solute is:
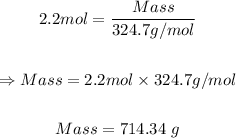
Therefore, the solute required to prepare 4.00 L of 0.55 M Hg(NO3)2 solution = 714.34 grams.