All the items use the same form of exponential equation:
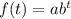
In this form, the initial value is always "a", because for t = 0:
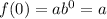
And whether it is a exponential growth of decay we can see by the "b" value.
It is an exponential growth if:
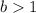
And it is an exponential decay if:
![0Now, for the alternatives.<p>a)</p>[tex]\begin{gathered} a=2 \\ b=(2)/(5) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/xia3lf9r1rbokfsa6t96jow1uywsv2soos.png)
So the initial value is 2 and "b" is less than 1, so it is an exponential decay.
b)
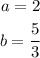
So the initial value is 2 and "b" is greater than 1, so it is an exponential growth.
c)
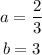
So the initial value is 2/3 and "b" is greater than 1, so it is an exponential growth.
d)
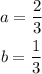
So the initial value is 2/3 and "b" is less than 1, so it is an exponential decay.
e)
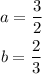
So the initial value is 3/2 and "b" is less than 1, so it is an exponential decay.