In the inelastic collision, the momentum of the system is conserved before and after the collision.
The objects stick together in the final state, thus, the velocity of both the object in the final state is the same.
In the second case,
According to the law of conservation of momentum, the velocity of each object is,
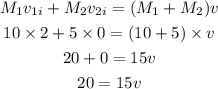
By simplifying,
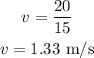
Thus, the final velocity of both the objects is 1.33 m/s.
In the third case,
According to the law of conservation of momentum, the velocity of each object is,
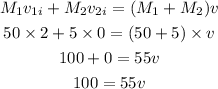
By simplifying,
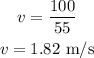
Thus, the final velocity of both the objects is 1.82 m/s.