They tell us that inside a balloon we have air. Air is a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen, having a low pressure we can assume that there is no interaction between these atoms or between molecules so we can apply the ideal gas law to calculate the final volume. The ideal gas law tells us:
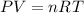
Where,
P is the pressure of the gas
V is the volume of the gas
n is the moles of the gas
R is a constant
T is the temperature of the gas
Now we have two states one initial with the following conditions:
T1=24°C =297.15K
V1=0.95L
And an end state:
T2=7°C=280.15K
V2=?
Now, we are told that the pressure remains constant and if we assume that the balloon has no gas inlets or outlets we can say that the moles remain constant as well.
If we substitute the values we know in the ideal gas equation we have:
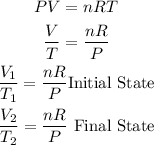
We can equate the two states since the ratio nR/P remains constant.
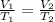
We clear V2,
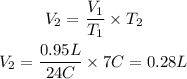
The volume of air bubble at 7°C is 0.28L