The probability of 2 consecutive events is the product of the probabilities of the single events.
The probability (P) of a single event A is:
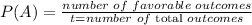
So, let's find the probability of the first event:
Event: Landing on a number less than 6.
Number of Favorable outcomes: 2 (Landing on 6 or 7).
Total outcomes: 3 (Landing on 6, 7, or 8).
Then,
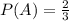
Now, let's find the probability of the second outcome:
Number of Favorable outcomes: 1 (Landing on 6 ).
Total outcomes: 3 (Landing on 6, 7, or 8).
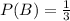
Then, the probability of landing on a number less than eight and then landing on a 6 is:
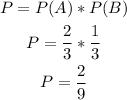
Answer: 2/9.