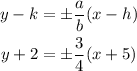Given the graph of the hyperbola:
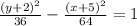
The general equation of the given hyperbola is:
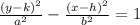
Where (h, k) is the center of the hyperbola
So, by comparing the equations:
Center = (h, k) = (-5, -2)
The hyperbola opens up and down
Since a =
![a=\sqrt[]{36}=6](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/2v2impsqh46onhoo4hlhkqkljo8cja7vf5.png)
The coordinates of the vertices are: (h, k + a ) and (h, k - a)
h = -5, k = -2, a = 6
So, the coordinates are:
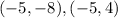
The slopes of the asymptotes are:
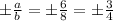
The equation of the asymptotes are: