The mass of the frog, m₁=3.9 kg
The mass of the skateboard, m₂=2.7 kg
Let us assume that the right is positive and the left is negative.
Thus the speed of the skateboard, u=-2.3 m/s
The initial momentum of the frog and the skateboard, p=0 kg·m/s²
From the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum of a system remains constant. That is, the sum of the momentum of the frog and the momentum of the skateboard after the frog jumps should be equal to zero.
Thus,
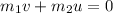
Where v is the horizontal velocity of the frog.
On substituting the known values in the above equation,
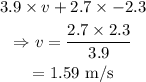
Thus the horizontal velocity of the frog is 1.59 m/s