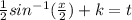Given:
The acceleration of the particle is,
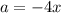
The particle was in origin with velocity,
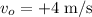
To find:
a) Find velocity as a function of x
b) Maximum position of the particle
c) Position as a function of time.
Step-by-step explanation:
(a)
The acceleration is,
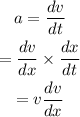
According to the question,
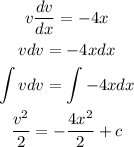
Here, 'c' is the integration constant.
Now, applying the condition at the origin, we can write,
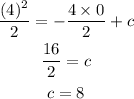
Now, the velocity is,
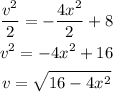
Hence, the velocity as a function of x is,
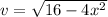
(b)
At the maximum position, the speed of the particle becomes zero.
So, the maximum position is,
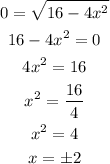
Hence, the position of the particle is,
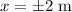
(c)
Now, the velocity of the particle is,
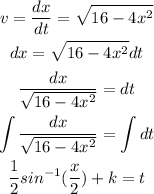
Here, 'k' is the integration constant.
Hence, the position as a function of time is,