The first given inequality is
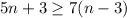
First, we use the distributive property

Second, we subtract 7n on each side
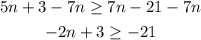
Third, we subtract 3 on each side
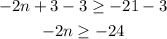
At last, we divide the inequality by -2, which changes the inequality sign
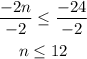
Therefore, the solution is all real numbers less than or equal to 12.
We repeat the process for the other inequalities.
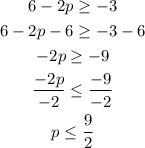
The solution is all real numbers less than or equal to 9/2.
The last inequality would be
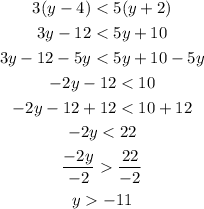
The solution is all real numbers greater than -11.