Notice that
![f(-5)=(2(-5)^2+3(-5)+1)/((-5)^2+5(-5))=(50-15+1)/(0)=(36)/(0)\rightarrow\text{ undefined}]()
Therefore, f(-5) is not a real number.
2) Calculating the limit when x->a from the left and right,
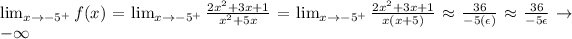
Because x^2+5x=x(x+5), and approaching from the right (x+5)>0; therefore, in the limit f(x)->-infinite
ϵ is a small positive number that approaches zero as a->-5
Similarly, in the case of approaching x->-5 from the left,
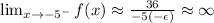
Therefore, since the limits approaching x->-5 from the left and right are not the same,
the limit of f(x) when x->-5 does not exist.
The function is not continuous at x=a and, furthermore, the limit of f(x) when x->-5 does not exist.