To determine the value of sin (θ + β), we can apply the trigonometric identity:
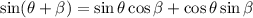
Since we already have the value for cosθ, let's find out sin θ.
Based on trigonometric identity,
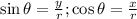
Based on the given value of cosθ, x = -√2 while r = 3. To determine the value of y, let's apply the Pythagorean Theorem.
![\begin{gathered} y=\sqrt[]{r^2-x^2} \\ y=\sqrt[]{3^2-(-\sqrt[]{2})^2} \\ y=\sqrt[]{9-2} \\ y=\sqrt[]{7} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/42ejlcjx5vc2zlftrueagepc4f576nj41c.png)
Since the given interval is between π and 3π/2 which is in Quadrant 3, y = -√7. Hence, the value of sin θ is:
![\sin \theta=-\frac{\sqrt[]{7}}{3}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/mrrqtvrujisogrr538xe2wc0qnfj4p3ccg.png)
The next thing that we shall solve is sin β and cos β. We can use the given tangent function to determine this.
![\begin{gathered} \text{tan}\beta=(y)/(x)=(4)/(3) \\ \text{Solve for r.} \\ r=\sqrt[]{x^2+y^2}=\sqrt[]{3^2+4^2}=\sqrt[]{9+16}=\sqrt[]{25}=5 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/3k4xvzfuzoydhscxmuncc6xkc3anw2lo9b.png)
Given the interval for beta, the angle is found in Quadrant 1. So, the values of sin β and cos β are:
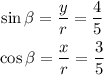
Now that we have the values for sin θ = -√7/3, cos β = 3/5, cos θ = -√2/3, and sin β = 4/5, let's plugged them into the first trigonometric identity we mentioned above.
![\begin{gathered} \sin (\theta+\beta)=\sin \theta\cos \beta+\cos \theta\sin \beta \\ \sin (\theta+\beta)=(-\frac{\sqrt[]{7}}{3})((3)/(5))+(-\frac{\sqrt[]{2}}{3})((4)/(5)) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/v1736hi7bmbmjpe0hgob8g46058d955e8r.png)
Then, simplify.
![\sin (\theta+\beta)=-\frac{\sqrt[]{7}}{5}-\frac{4\sqrt[]{2}}{15}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/v5klb130uocibj7sj13nl34h231jxt6oeo.png)
The final answer is shown above.