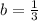Answer:
The value of b for the equation to have no solution is;
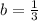
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the the equation;
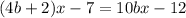
solving we have;
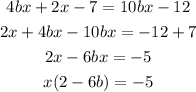
for x to have a solution, the product of x and (2-6b) must not be equal to zero.
So, the value of b for the equation to have no solution can be derived by equating (2-6b) to zero;
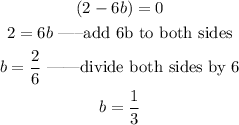
Therefore, the value of b for the equation to have no solution is;