Answer:
a. Increasing
b. Increasing
c. Decreasing
Step-by-step explanation:
Part A (g(x) = 4x – 2)
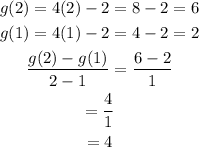
g(x) is increasing since its rate of change is positive.
Part B (f(x) = 3x)
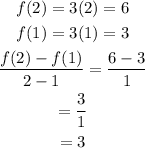
f(x) is increasing since its rate of change is positive.
Part C (h(x) = 2-x)
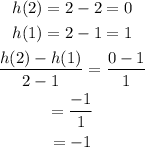
h(x) is decreasing since its rate of change is negative.