Step 1 - Finding valence electrons
Let's use the first molecule, water, as an example of how to proceed to find the required properties. To find the valence electrons of each atom, we must consider their electronic configuration.
The molecule of water has O as well as H atoms. Their electronic configuration is:
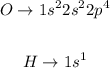
Note that the valence shell is the 2nd shell for O, but the 1st shell for H. Therefore, O has 6 electrons in its valence shell, whereas H has only one.
Step 2 - Determining the Lewis structure
To determine the Lewis structure we can use a very useful tip:
The atom which makes the greatest number of bonds goes in the middle.
It's not a rule, just a tip. But it may work wonders. In the case of H2O, the atom that makes the most bonds is O, so:
Let's remember how may bonds each element makes:

The next step is a little bit like Lego playing. We must try to join the atoms together respecting the number of bonds each needs to do. For water, the only possible solution is:
Remember O has 6 electrons in its valence shell. Two of them are participating in a covalent bond, while 4 are remaining. Let's include the remaining electrons:
Step 3 - Finding the shape
To find the shape (geometry) of a molecule, we use the VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) Theory.
Note: VSEPR states that the electrons in a covalent bond, as well as the remaining non-bonding electron pairs repulse each other. As a consequence, the molecule will adopt the geometry that minimizes the repulsion between the bonding and valence electrons.
Since water is a three atom molecule, and since there are remaining electron-pairs in the middle atom (O), its geometry will not be linear. The remaining valence electrons of O will cause the bonding electrons to "bend", i.e., to move farther away, due to repulsion. The molecule thus becomes angular: