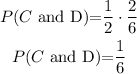Answer:
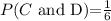
Explanation:
Probability is represented by the following equation:
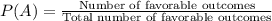
Therefore, for this situation:
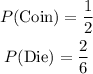
Since the probability of two events occurring together but independents is represented by the multiplication of the probabilities of the events: