This is a conditional probability problem
The conditional probability of A given B, denoted P(A|B), is the probability that event A has occurred in a trial of a random experiment for which it is known that event B has definitely occurred. It may be computed by means of the following formula:
To determine P(A|B)
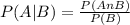
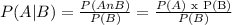
Since P(A) = 0.55 and P(B)=0.72
So,
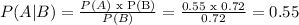
P(A|B) =0.550 (To the nearest thousandth)