Answer:
Question A)
For Object A
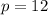 kg*m/s
kg*m/s
For Object B
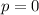 kg*m/s
kg*m/s
Question B)
12 kg*m/s
Question C)
4.5 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
The principle of conservation of momentum states that in a system make out of objects that react (collide or explode), the total momentum is constant if no external force is acted upon the system.
Sum of Momentum Before Reaction = Sum of Momentum After Reaction
Here is the formula
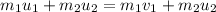
Note the following.
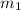 = mass of first object
= mass of first object
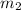 = mass of second object
= mass of second object
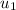 = initial velocity of first object
= initial velocity of first object
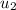 = initial velocity of the second object
= initial velocity of the second object
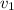 = final velocity of the first object
= final velocity of the first object
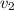 = final velocity of the second object
= final velocity of the second object
In our case, let Object A be the first object and let Object B be the second object.
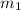 = 3 kg
= 3 kg
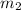 = 2 kg
= 2 kg
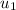 = 4 m/s
= 4 m/s
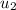 = 0 m/s
= 0 m/s
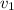 = 1 m/s
= 1 m/s
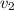 = ? m/s
= ? m/s
Lets enter our values into the equation
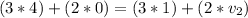
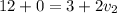
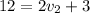
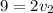

Now we have all the information we need to answer the questions.
Question A) What is the initial momentum of object A and object B?
The linear momentum formula is
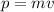
For Object A
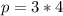
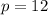 kg*m/s
kg*m/s
For Object B
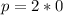
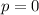 kg*m/s
kg*m/s
Question B)
12 kg*m/s + 0 kg*m/s
12 kg*m/s
Question C)
Part I.
For Object A
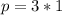
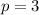 kg*m/s
kg*m/s
For Object B
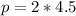
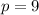 kg*m/s
kg*m/s
Part II.
The velocity of Object B after the collision is 4.5 m/s.