A dilation is a transformation that produces an image that is the same shape as the original, but is a different size.
A dilation stretches or shrinks the original figure. A description of a dilation includes the scale factor (or ratio) and the center of the dilation.
To perform the expansion, each point must be multiplied by the expansion factor or ratio
1) Dilation of 0.25
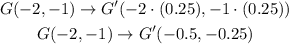
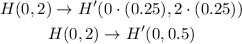
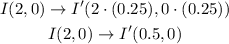
Graphically you can see the dilation:
3) Dilation of 2
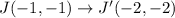
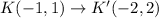
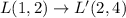
Graphically you can see the dilation