Solution
we are given the two linear equations
First Equation
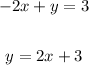
Second Equation
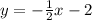
Let mA and mB denotes the gradient of the first and second equation respectively written as
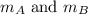
Using the slope - intercepty form, one can see that
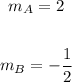
Now,
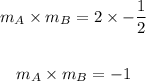
Therefore, the lines are Perpendicular
Option B