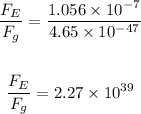Answer:
The ratio of the greater force to the lesser force is:
Step-by-step explanation:
The masses of protons and electron, and the distance between them are given below.
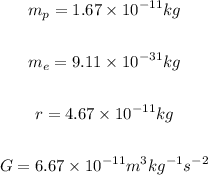
The gravitational force between the proton and electron is calculated below
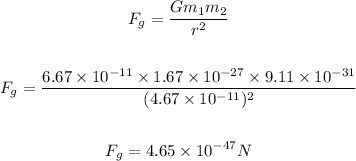
The magnitude of the charge on a proton and an electron is the same, and is given as:
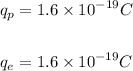
The electrostatic force between the proton and electron is then calculated as:
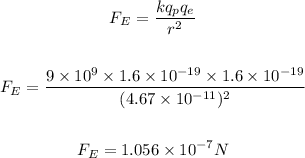
As seen above, the electrostatic force is the greater force, while the gravitational force is the lesser force
The ratio of the greater to the lesser force is: