The given problem can be exemplified in the following free-body diagram:
Now we sum the forces in the horizontal direction:
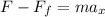
Where:

Since the movement is required to be at a constant speed the acceleration must be zero, therefore:
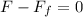
Now we solve for the force "F":
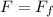
Now we use the following definition of friction:
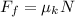
Where:
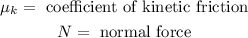
The kinetic friction coefficient is used due to the fact that we are considering the body as it is already in movement.
Replacing in the sum of horizontal forces:
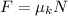
Now, to determine the value of the normal force we will add the forces in the vertical direction:
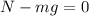
The vertical forces add up to zero because there is no vertical movement. Now we solve for the normal force "F":
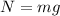
Now we replace in the sum of horizontal forces:
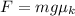
Now we plug in the values:
![F=(20\operatorname{kg})(10(m)/(s^2))(0.6)]()
Solving the operations we get:
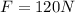
Therefore, a force of 120 Newtons is required.