ANSWER
![x=(1)/(2)+\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}\text{ and }x=(1)/(2)-\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8oh6lwadi6konel5k5ybqv0sbsapus368h.png)
Step-by-step explanation
Given the equation,
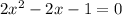
We have to solve it for x.
We can solve this using the quadratic formula,
![\begin{gathered} ax^2+bx+c=0 \\ x=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/uuterq6bz1kwr2mb9jy58c523r5v4v644y.png)
In our equation a = 2, b = -2 and c = -1,
![x=\frac{2\pm\sqrt[]{(-2)^2-4\cdot2\cdot(-1)}}{2\cdot2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/gu0st4acwwyh1yd3rlwbmrdh3kahp2o7it.png)
![x=\frac{2\pm\sqrt[]{4+8}}{4}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/kdusqb73fhjup86okvroocikwem7ff3jhx.png)
![x=\frac{2\pm\sqrt[]{12}}{4}=\frac{2\pm\sqrt[]{4\cdot3}}{4}=\frac{2\pm2\sqrt[]{3}}{4}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/wyv6c5t0z2vqletu0mugvgegednq3tdeyx.png)
Distribute the denominator into the addition/subtraction,
![x=(2)/(4)\pm\frac{2\sqrt[]{3}}{4}=(1)/(2)\pm\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ec6kcxeqd3ign1a52i2hcc6x3hstcws2fc.png)
The values of x that are solution to this equation are,
![x=(1)/(2)+\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}\text{ and }x=(1)/(2)-\frac{\sqrt[]{3}}{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/8oh6lwadi6konel5k5ybqv0sbsapus368h.png)