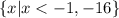Solution:
Given:
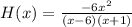
The domain of a function is the set of input values that make the function real and defined.
Hence, we need to find the singularity or undefined points of the function.
The function H(x) will be undefined when the denominator is 0.
Thus, singularity exists at;
![\begin{gathered} Equating\text{ the denominator to 0,} \\ (x-6)(x+1)=0 \\ x-6=0,x+1=0 \\ x=6,x=-1 \\ \\ Hence,\text{ undefined points exists at }x=6\text{ and }x=-1 \end{gathered}]()
The function is therefore defined at all other values except at the undefined points.
Hence,

Therefore, the domain of the function H(x) is;