In general, a polynomial of degree 3 is given by the next expression
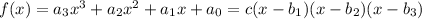
Where b_1, b_2, and b_3 are the roots of the polynomial.
Therefore, in our case,
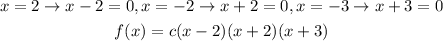
We need to find the value of c.
For this, notice that the f(0)=4
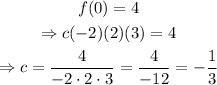
Therefore,
![\begin{gathered} f(x)=-(1)/(3)(x-2)(x+2)(x+3)=-(1)/(3)(x^2-4)(x+3)=-(1)/(3)(x^3+3x^2-4x-12)=-(x^3)/(3)-x^2+(4x)/(3)+4 \\ \end{gathered}]()
The answer is f(x)=(-1/3)(x-2)(x+2)(x+3), which is equivalent to -x^3/3-x^2+4x/3+4