Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The question requires us to calculate the amount of moles of H2O that could be produced from the given amounts of H2 and O2.
The following information was provided by the question:
mass of H2 = 50.0g
mass of O2 = 80.0g
balanced chemical equation: 2 H₂(g) + O₂(g) → 2 H₂O(g)
We'll need to go through the following steps to solve this problem:
1) Calculate the number of moles of H2 and O2, considering the masses given and their respective molar masses;
2) Identify the limiting and excess reactant, considering the amount of H2 and O2 and the balanced chemical equation;
3) Calculate the amount of H2O that could be produced from the limiting reactant identified in the previous step.
Next, we'll go through the steps above to solve the problem:
1) We can obtain the number of moles of H2 and O2 applying the following equation:
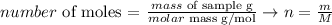
The molar mass of H2 and O2 is 2.016 g/mol and 31.98 g/mol, respectively. Thus, we can calculate their number of moles:
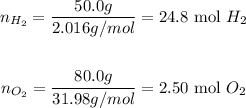
Therefore, considering the mass provided by the question, 24.8 moles of H2 and 2.50 moles of O2 were used in the reaction.
2) Next, we need to identify which of the reactants is the limiting one, considering the amounts of reactants used and the balanced chemical equation.
According to the reaction, 2 moles of H2 are necessary to react with 1 mol of O2. Thus, we can calculate how many moles of H2 would be necessary to completely react with 2.50 moles of O2:
2 mol H2 -------------------------- 1 mol O2
x -------------------------------------- 2.50 mol O2
Solving for x, we'll have:
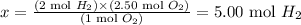
Therefore, 5.00 moles of H2 would be necessary to completely react with 2.50 moles of O2. Since the amount of H2 used was greater than the required amount (24.8 moles used > 5.00