Answer:
1. 5.03 m/s
2. 4.06 m/s
3. 683.46 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
Part 1.
Since the tennis ball is dropped, we can calculate the final velocity using the following equation.
![v_{}=\sqrt[]{2gh}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/nnwwo47ik6ulkm0op39jf4cu7digwdpkzy.png)
Where g is the acceleration of gravity and h is the height. So, replacing the values, we get:
![\begin{gathered} v_{}=\sqrt[]{2(9.8)(1.29)} \\ v=5.03\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/clqnw2uf2b9orz67urejekcc7d126aq7ho.png)
Then, the tennis ball hits the ground at 5.03 m/s
Part 2.
Now, we can use the same equation from part 1 but the height this time will be equal to 0.839 m, then, the velocity is equal to:
![\begin{gathered} v=\sqrt[]{2(9.8)(0.839)} \\ v=4.06\text{ m/s} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/dnwx0yz37utqyjcpme0gidy91q4i0a6yla.png)
So, the tennis ball leaves the ground at 4.06 m/s
Part 3.
Finally, the acceleration is equal to the change in velocity over time, so:
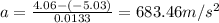
Therefore, the acceleration given to the tennis ball by the ground is 683.46 m/s²