The Solution:
Suppose we have a function given as below:
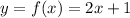
Whatever values x takes are examples of domain input while the corresponding values of y for each value of x are examples of range output. For example, let the values of x be -1, 0, 1, 2,... So, the corresponding values of y will be
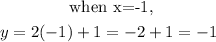
When x =0,
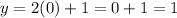
When x = 1
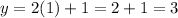
When x = 2
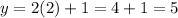
So,
Domain input = {-1, 0, 1, 2,...}
Range output = {-1, 1, 3, 5,...}