Given the equation:
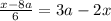
To solve for x, first we move the 6 to the other side of the equation:
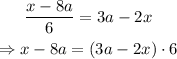
Since the 6 was dividing, we pass it to the other side multiplying. Now we apply the distributive property and move the term -8a to the other side:
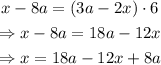
Finally, we move the -12 to the other side with its sign changed:
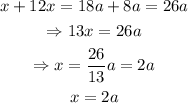
therefore, x=2a